This article will talk about on how to capture and analyze Wireshark logs, lets see it step by step
Wireshark logs capture
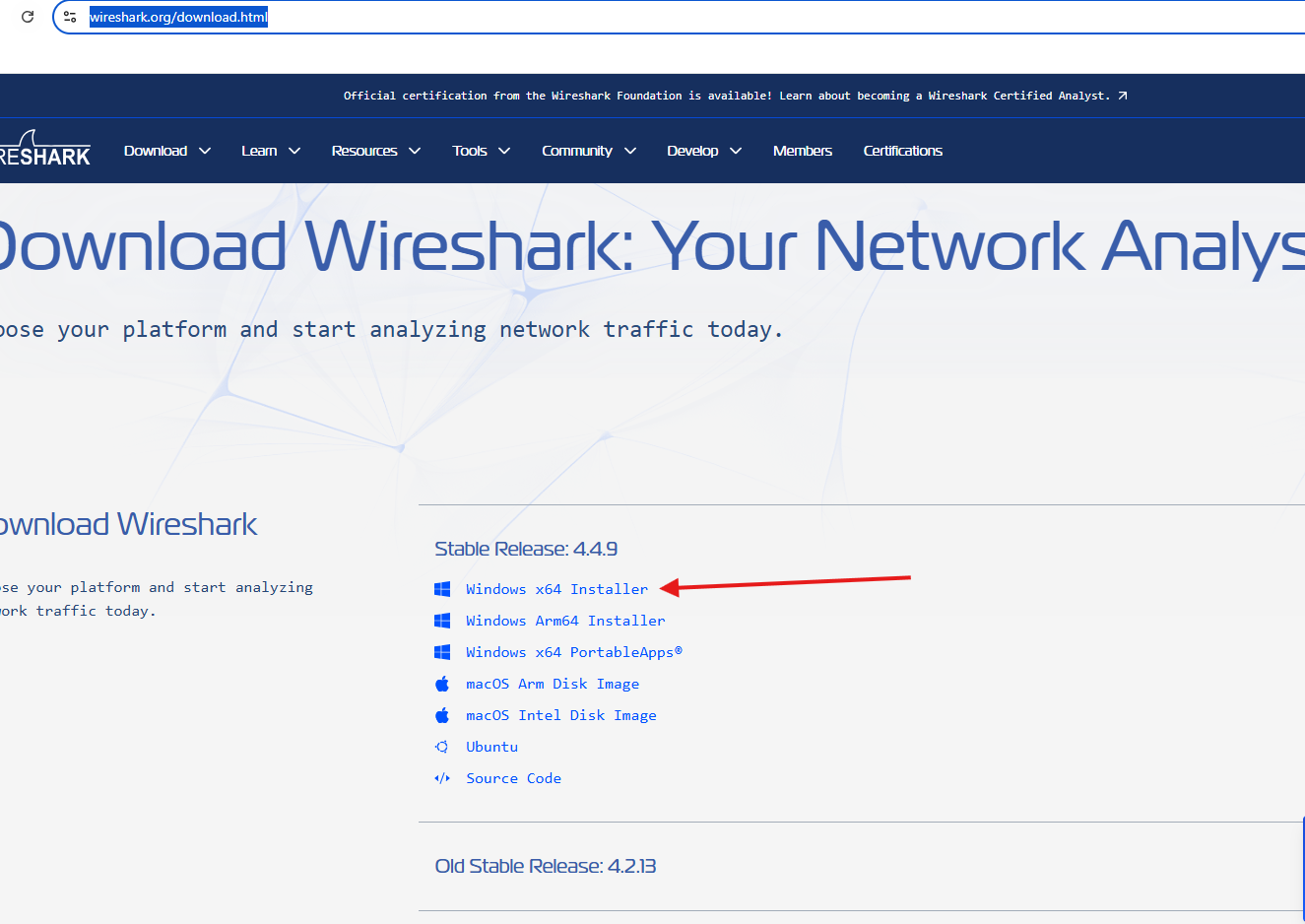
Open this link : https://www.wireshark.org/download.html
I will install this build as per my machine’s make n model, you choose yours’s accordingly
let it get install
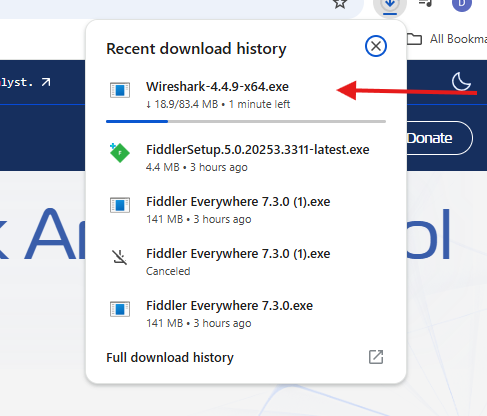
then go to the downloads folder and look for .exe –> double click and start installing it
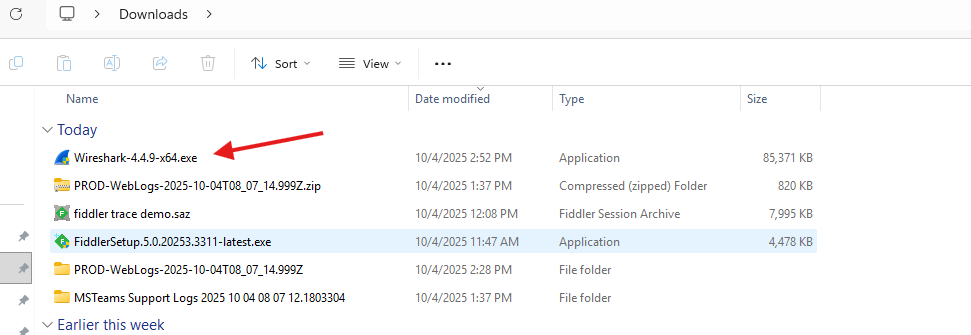
I am going with the default settings
Here installation is done
Now launch the Wireshark app
Hit control + A –> it will select all interfaces

then click on the blue-fin to start collecting the logs
I have called to one of the user to reproduces the issue once issue is reproduced hit stop button
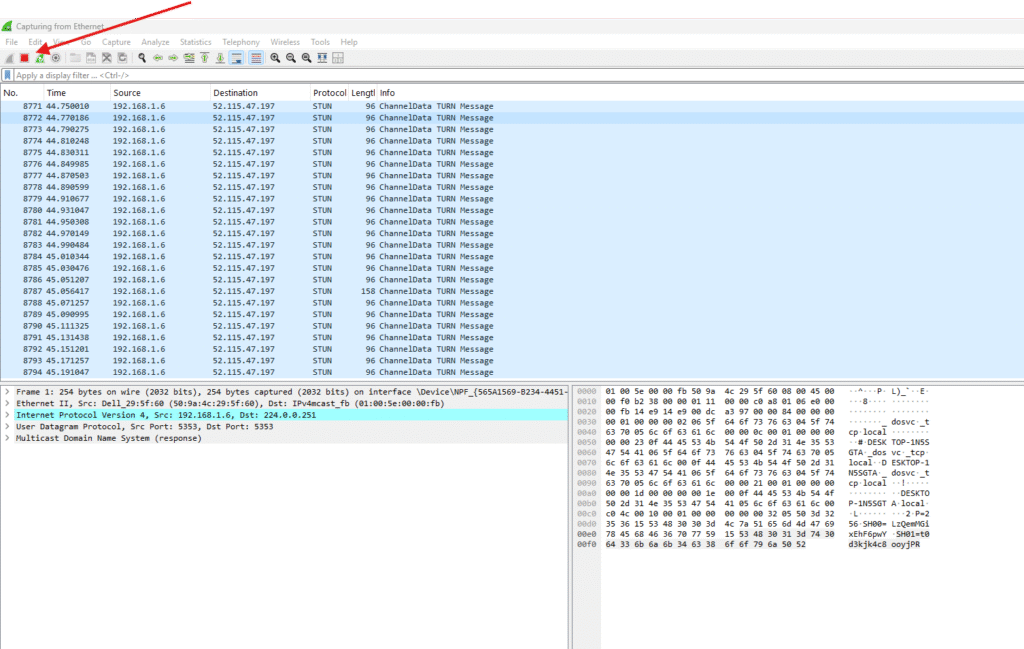
Go to files option and save the logs first
Wireshark logs analysis:
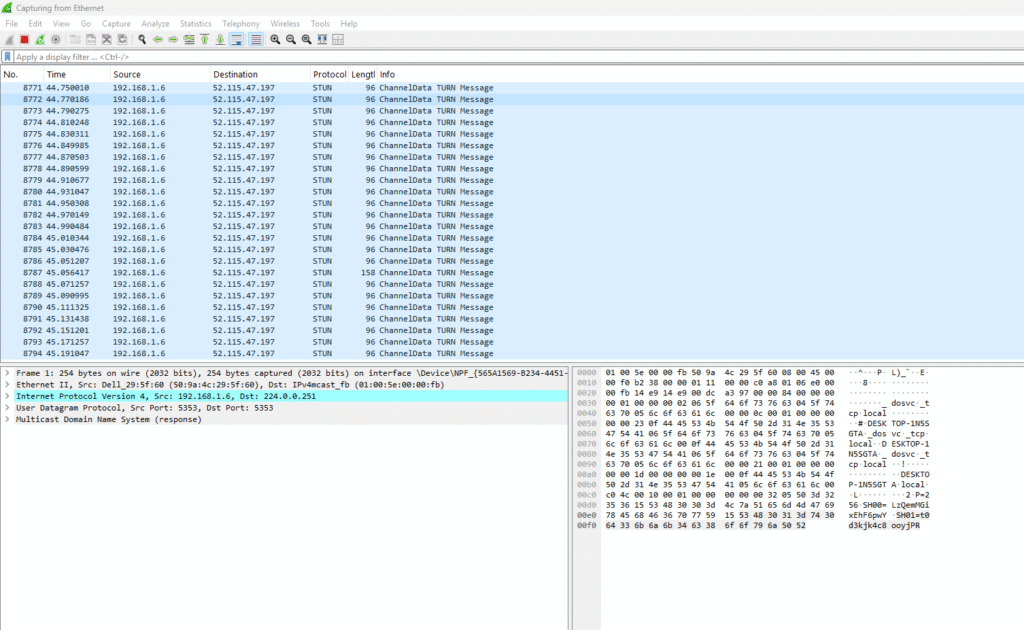
I have used this filter udp.port==3479 while analyzing the logs as I made the audio call to admin user
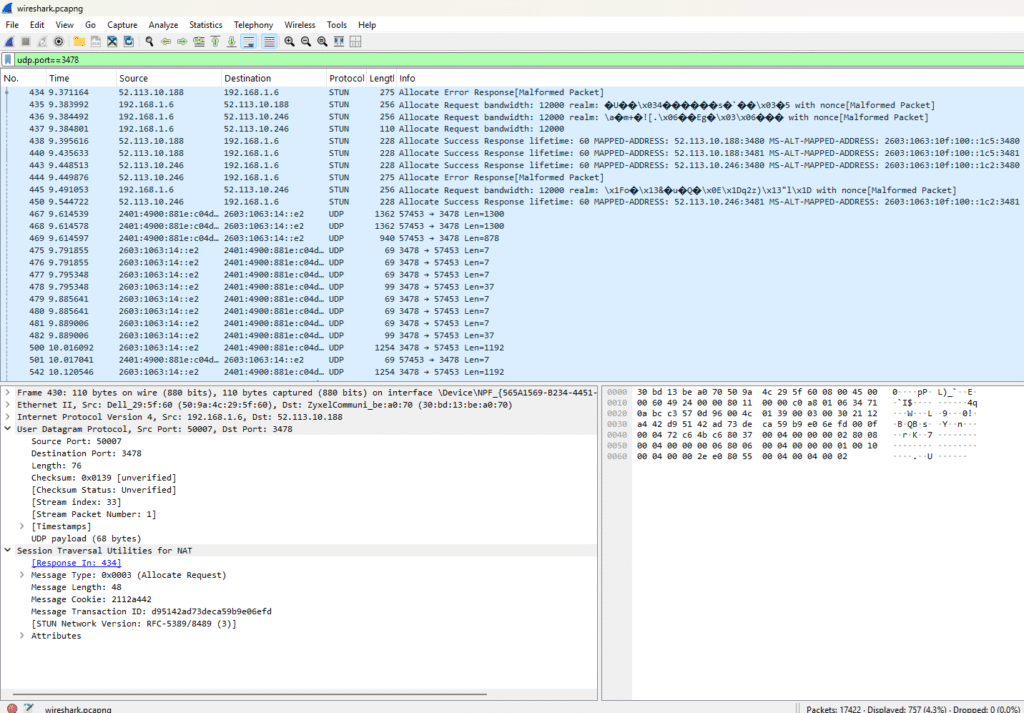
we can clearly see the STUN and UDP traffic in the logs
We have to use different different filters as per the requirements please see below some imp filters can be used.
Imp filters to use in Wireshark logs
By Protocol:
http or dns: Shows only HTTP or DNS traffic, respectively.
!(arp or icmp or dns): Excludes ARP, ICMP, and DNS traffic, focusing on other protocols.
By IP Address:
ip.addr == : Displays packets to and from a specific IP address.
ip.src == : Shows packets originating from a specific IP address.
ip.dst == : Shows packets destined for a specific IP address.
By Port Number:
tcp.port == 80: Isolates HTTP traffic on port 80.
tcp.port == 443: Isolates HTTPS traffic on port 443.
tcp.port in {80 443 8080}: Filters for TCP traffic on multiple specified ports.
By Connection or Stream:
tcp.stream eq : Follows a specific TCP stream.
By TCP Flags:
tcp.flags.reset == 1: Shows all TCP reset packets, useful for identifying abrupt connection terminations.
By String Content:
frame contains “”: Displays packets containing the specified keyword.
frame matches “”: Performs a case-insensitive search using a regular expression.
Parallelly you can also collect the fiddler trace : https://microbrother.com/fiddler-trace-how-to-capture-and-analyze-it/ to deep dive into the issue.
Conclusion:
Post reading above article reader will be able to capture and analyze the Wireshark logs.
Thank you ☺️